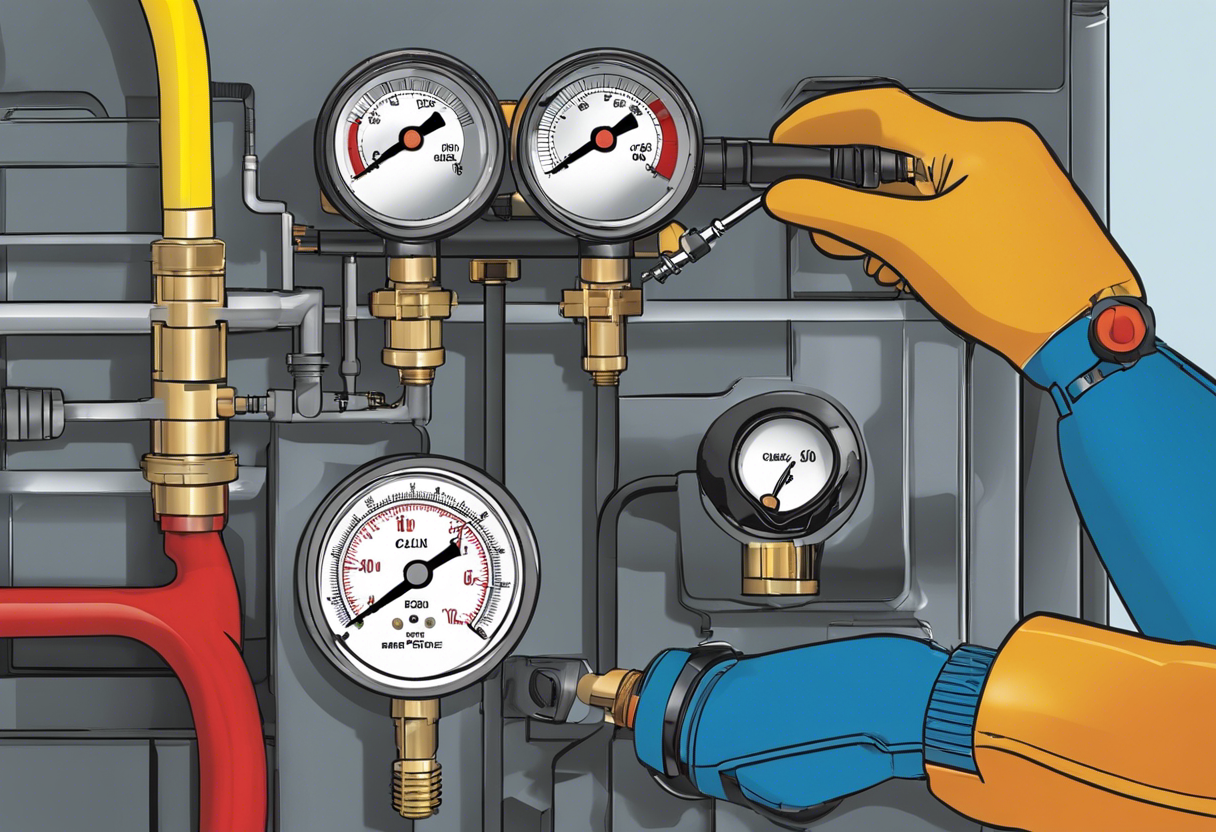
Fuel pressure regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of a vehicle’s fuel system. Here are the key points to know about it:
- Function: Fuel pressure regulators are responsible for maintaining a consistent fuel pressure within the fuel system. They achieve this by regulating the flow of fuel to the engine based on factors such as engine load and speed.
- Location: They are typically located near the fuel rail or the fuel line within the engine compartment. Some vehicles may have the regulator integrated into the fuel pump assembly.
- Components: A typical fuel pressure regulator consists of a housing, a diaphragm, a spring, and a vacuum/pressure reference port. The spring exerts pressure on the diaphragm, which in turn controls the flow of fuel.
Understanding the basics of regulators is essential for diagnosing fuel system issues accurately. Understanding the Function of a Regulator
A fuel pressure regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of a vehicle’s fuel system. Here are some key points to understand its function:
- Regulating Fuel Pressure: The primary function of a regulator is to maintain a consistent fuel pressure to the engine. This is essential for the engine to perform efficiently and prevent any damage due to either insufficient or excess fuel pressure.
- Maintaining Optimal Fuel Flow: By regulating the fuel pressure, the fuel pressure regulator ensures that the right amount of fuel is delivered to the engine at all times. This helps optimize fuel efficiency and engine performance.
- Preventing Fuel Overflow: In case there is a sudden increase in fuel pressure, the regulator diverts the excess fuel back to the fuel tank. This prevents any overflow or leakage of fuel, which could be dangerous and wasteful.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator
- The engine experiencing difficulty starting or taking longer to start than usual.
- Variation in engine performance, such as rough idling or stalling when driving.
- Decreased fuel efficiency, which can be noticed through increased fuel consumption.
- Black smoke emitting from the exhaust pipe due to a rich fuel mixture.
- Strong smell of gasoline around the vehicle, indicating a potential fuel leak.
- Engine misfires or backfires, especially under acceleration.
- Sudden loss of power while driving, particularly when going uphill or during acceleration.
- The Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminating on the dashboard, signaling potential issues with the fuel system.
- Engine hesitation or surging, where the vehicle feels like it is lurching forward or stalling intermittently.
Note: It is essential to address these symptoms promptly to prevent further damage to the vehicle’s fuel system and engine components.
How to Diagnose a Faulty Pressure Regulator
- Check for engine performance issues: A faulty fuel pressure regulator can cause engine performance issues such as poor acceleration, stalling, or rough idling. If you notice any of these symptoms, it could indicate a problem with the regulator.
- Inspect for fuel leaks: Look for any signs of fuel leaks around the regulator. Leaking fuel can indicate a fault in the regulator or its components. Ensure to address any leaks promptly to prevent safety hazards.
- Test fuel pressure: Using a fuel pressure gauge, test the pressure in the fuel system. A faulty fuel pressure regulator can result in low or inconsistent fuel pressure readings, affecting the engine’s performance. Comparing the measured pressure with the manufacturer’s specifications can help identify any issues.
- Listen for unusual sounds: A faulty regulator may produce unusual sounds such as a hissing noise coming from the fuel system. Pay attention to any unfamiliar sounds while the engine is running, as they can signal a problem with the regulator.
- Inspect vacuum line: Check the vacuum line connected to the fuel pressure regulator for any signs of damage or wear. A vacuum leak in the line can affect the regulator’s operation and lead to fuel pressure irregularities. Replace the line if necessary.
- Consult a professional: If you are unable to diagnose the issue with the regulator or if you suspect a fault but are uncertain, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic. They can perform a thorough inspection and provide recommendations for repairs or replacements.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose a faulty fuel pressure regulator and address any issues to ensure optimal engine performance and safety.
The Importance of Addressing a Faulty Pressure Regulator
- Engine Performance: A faulty regulator can lead to a variety of engine performance issues, such as rough idling, stalling, misfiring, and overall poor acceleration. Addressing this issue is crucial to ensure optimal engine performance and efficiency.
- Fuel Efficiency: When the is not functioning correctly, it can cause an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. By addressing this issue promptly, drivers can improve their vehicle’s fuel economy and save on gas expenses.
- Prevention of Further Damage: Ignoring a faulty fuel pressure regulator can result in more severe damage to other engine components over time. By addressing the issue early on, drivers can prevent potential costly repairs and ensure the longevity of their vehicle.
- Emissions Compliance: A malfunctioning regulator can impact the vehicle’s emissions output, potentially causing it to fail emissions tests. Addressing this issue promptly is important to ensure that the vehicle remains compliant with emissions regulations and environmental standards.
- Safety Concerns: In certain situations, a faulty regulator can lead to safety concerns, such as sudden stalling or loss of engine power while driving. Addressing this issue promptly is essential to ensure the safety of the driver, passengers, and other road users.
It is vital for vehicle owners to be aware of the importance of addressing a faulty fuel pressure regulator promptly to maintain optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, prevent further damage, ensure emissions compliance, and prioritize safety on the road.
Replacing a Faulty Pressure Regulator
When dealing with a faulty fuel pressure regulator, it is essential to address the issue promptly and efficiently to ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle. Here are the steps to replace a faulty regulator:
- Step 1: Gather the necessary tools: Before beginning the replacement process, make sure you have the required tools on hand. This may include safety gloves, safety goggles, a wrench set, and a new fuel pressure regulator.
- Step 2: Locate the fuel pressure regulator: The regulator is typically located near the fuel injectors or on the fuel rail. Consult your vehicle’s manual if you are unsure of its exact location.
- Step 3: Depressurize the fuel system: Before removing the old regulator, it is crucial to relieve the pressure in the fuel system. This can be done by disconnecting the fuel pump fuse and running the engine until it stalls.
- Step 4: Remove the old regulator: Using the appropriate tools, carefully disconnect the electrical connector and fuel lines attached to the old fuel pressure regulator. Then, remove the regulator from its mounting location.
- Step 5: Install the new regulator: Place the new regulator in the correct position and reattach the electrical connector and fuel lines. Ensure everything is securely fastened.
- Step 6: Test the new regulator: Once the new regulator is installed, start the engine and check for any leaks or irregularities in the fuel system. If everything looks good, you have successfully replaced the faulty regulator.
Maintaining a Pressure Regulator for Longevity
-
Regular Inspection:
- Check for any signs of leaks or corrosion on the regulator.
- Inspect the vacuum hose for cracks or damage that could affect performance.
-
Fuel Filter Replacement:
- Replace the fuel filter according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedule.
- A clogged fuel filter can put extra strain on the regulator, leading to issues.
-
Keep Fuel Clean:
- Use high-quality fuel to prevent debris buildup in the regulator.
- Contaminants in the fuel can damage the regulator over time.
-
Avoid Over-Pressure:
- Ensure the fuel pressure is within the manufacturer’s specified range.
- Excessive pressure can cause the regulator to fail prematurely.
-
Professional Inspection:
- If experiencing issues, have a certified mechanic inspect the regulator.
- Early detection of problems can prevent major damage and costly repairs.
-
Proper Installation:
- Ensure the regulator is installed correctly to avoid leaks or malfunctions.
- Incorrect installation can lead to fuel system problems down the line.
Signs of a Failing Pressure Regulator in Diesel Engines
- Sudden Loss of Power:
- One of the key indicators of a failing fuel pressure regulator in diesel engines is a sudden loss of power during acceleration. This could be due to the regulator not maintaining the required pressure for optimal performance.
- Hard Starting:
- Difficulty starting the diesel engine, especially when cold, can be a sign of a faulty regulator. If the regulator is not delivering the correct fuel pressure to the engine, it can result in hard starting issues.
- Black Smoke from Exhaust:
- Another common symptom of a failing regulator is the presence of black smoke coming from the exhaust. This indicates that the engine is running rich, which can be caused by excess fuel due to a malfunctioning regulator.
- Engine Stalling:
- A failing regulator may cause the engine to stall unexpectedly. This can happen when the regulator is unable to maintain consistent fuel pressure, leading to fuel delivery interruptions and eventual stalling of the engine.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency:
- Decreased fuel efficiency, where the diesel engine is consuming more fuel than usual, can be attributed to a failing regulator. The improper regulation of fuel pressure can result in inefficient combustion and increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light:
- Often, a failing fuel pressure regulator will trigger the check engine light on the dashboard. This serves as an important warning sign and should prompt immediate diagnostic attention to avoid further damage to the diesel engine.
Signs of a Failing Pressure Regulator in Gasoline Engines
- Sudden decrease in fuel efficiency: A failing fuel pressure regulator can cause the engine to receive too much or too little fuel, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. Monitoring your vehicle’s gas mileage can help in identifying this issue.
- Difficulty starting the engine: If the regulator is failing, it may not provide the correct amount of fuel to the engine during startup, resulting in difficulties starting the engine or prolonged cranking.
- Rough idling or stalling: Fluctuating or unusually high idle speeds, as well as the engine stalling while at a stop, could be signs of a failing regulator affecting the engine’s air-fuel mixture.
- Black smoke from the exhaust: Excessive black smoke coming from the tailpipe indicates an overly rich air-fuel mixture due to a faulty regulator, leading to inefficient combustion.
- Engine misfires: A failing fuel pressure regulator may disrupt the precise balance of fuel and air in the engine, causing misfires, hesitation, or jerking sensations while accelerating.
- Fuel leaks: Visible fuel leaks around the regulator or a strong smell of gasoline near the engine could indicate a failing regulator that is unable to maintain proper fuel pressure.
- Check Engine Light (CEL) comes on: The onboard diagnostics system may detect irregular fuel pressure caused by a failing fuel pressure regulator, triggering the Check Engine Light on the dashboard.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
- Checking the fuel pressure regulator is a crucial step in diagnosing potential fuel system issues in your vehicle.
- Regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent costly repairs and ensure optimal engine performance.
- Understanding the symptoms of a faulty regulator, such as poor fuel efficiency or engine misfires, can help you address the issue promptly.
- If you suspect a problem with your regulator, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic for a thorough diagnosis and repair.
- Remember to follow safety precautions when working with fuel systems and always refer to your vehicle’s specific repair manual for guidance.
- By taking proactive measures and staying vigilant, you can keep your fuel system in top condition and enjoy a smoother driving experience.
FAQs
Read More: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9QbdkGVX3W0
Read More: https://manualwheel.com/simpson-helmets-…and-buying-guide/